If you are familiar with the AWS services landscape, you might already know the Parameter Store (part of the AWS System Manager, in short, SSM). This service allows us to store parameters for our application as a String, StringList or SecureString (encrypted using KMS keys). We can use this AWS service to configure both plain text properties (e.g., name of a queue) and secrets (e.g., database passwords, OAuth2 credentials, etc.). With this blog post, you’ll learn how to configure your Spring Boot application to retrieve configuration properties from the AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store.
UPDATE: The configuration processing slightly changed with Spring Boot 2.4. Take a look at the last section that discusses how to include this functionality for recent Spring Boot versions.
Spring Boot Application Setup
For the demo application, we’re using Spring Boot 2.2.6 and Java 11. Besides the spring-boot-starter-web, the application includes two Spring Cloud AWS dependencies:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>de.rieckpil.blog</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-aws-ssm-parameter-resolving</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-boot-aws-ssm-parameter-resolving</name> <description>Resolving SSM parameters for a Spring Boot application</description> <properties> <java.version>11</java.version> <spring-cloud.version>Hoxton.SR3</spring-cloud.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-aws</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-aws-parameter-store-config</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Test Dependencies --> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> |
Configure Credentials to Access the AWS Parameter Store
First, we need to configure proper access from our Spring Boot application to AWS. For this, you’ll need to obtain credentials from your AWS account. You can follow the steps mentioned in this blog post to get them.
There are multiple ways to configure credentials for the underlying Amazon Java SDK. As we are using the Spring Cloud AWS Starter, we can specify the AWS access and secret key inside our application.properties or application.yml file using the cloud.aws.credentials namespace.
While this works well for other Spring Cloud AWS components (like SQS, S3, SNS, etc.), we can’t use it for the Parameter Store and Secrets Manager configuration. This is because both rely on the DefaultAWSCredentialsProviderChain by default. There are ways to override this (read the docs for more information), but for the sake of simplicity, we’ll use one of the providers of the default AWS provider chain.
The default AWS provider chain looks for the AWS credentials at the following places:
- Environment variables (
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEYorAWS_ACCESS_KEYandAWS_SECRET_KEY) - Java System Properties (
aws.accessKeyIdandaws.secretKey) - Credentials profile (default location is (
~/.aws/credentials) - Credentials delivered through the Amazon EC2 container service
- Instance profile credentials delivered through the Amazon EC2 metadata service
We’re going with the first approach and add two environment variables AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID & AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY to the launch configuration of the Spring Boot application in IntelliJ.
We can also set these variables in our current shell session (from which we start our application) or our whole system.
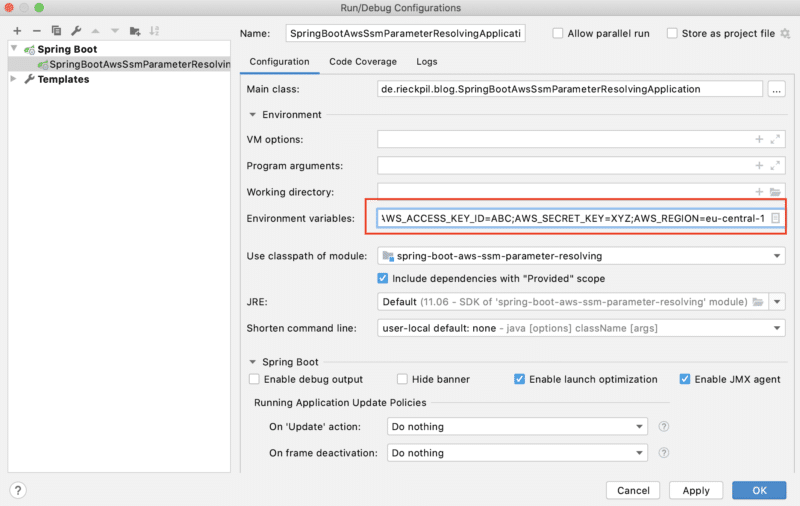
Resolve AWS Properties Inside Our Spring Boot Application
First, it’s important to configure the correct AWS region.
Make sure to use the same region where you created the parameters; otherwise, our Spring application won’t find them.
For the demo application, we’re using the AWS region eu-central-1 (Frankfurt, Germany) and set the region using the configuration property cloud.aws.region.static inside our application.yml:
|
1 2 3 4 |
cloud: aws: region: static: eu-central-1 |
Following the default convention, the parameters inside the Parameter Store require a specific naming structure:
|
1 |
/config/<name-of-the-spring-application>_<profile>/<parameter-name> |
We can configure the name of our Spring application inside the application.yml
|
1 2 3 |
spring: application: name: demo |
Given this structure, let’s define two parameters as SecretString for the default and production profile inside the AWS Systems Manager:
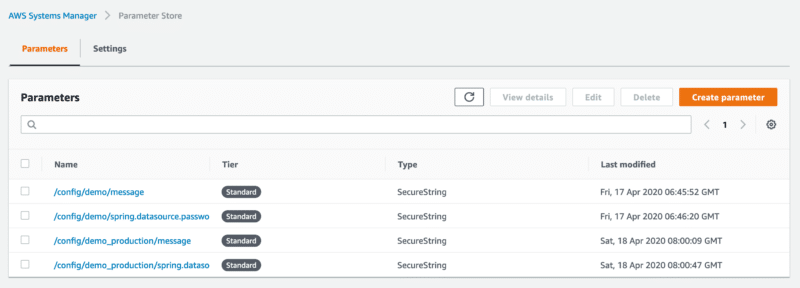
Note: You can omit the profile name for properties targeting the default profile.
Before we can start the application on a local machine, we ensure to disable the automatic stack detection inside the application.yml as we are not starting the application inside an AWS stack (e.g., on EC2):
|
1 2 3 4 |
cloud: aws: stack: auto: false |
Given this setup, the spring-cloud-starter-aws-parameter-store-config will now autoconfigure a AwsParameterStorePropertySourceLocator.
This class implements the PropertySourceLocator interface and Spring will use it to locate properties requested by the application e.g. @Value("${my.property}").
For a quick demo, let’s request both Parameter Store properties and print them during application startup:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
@Component public class ParameterResolveDemo implements CommandLineRunner { @Value("${message}") private String message; @Value("${spring.datasource.password}") private String dataSourcePassword; @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Message property: " + message); System.out.println("DataSource password property: " + dataSourcePassword); } } |
Running the application with the default profile results in the following log output:
|
1 2 |
Message property: Duke DataSource password property: sUp3rSeCuR3 |
… and using the production profile in the following:
|
1 2 |
Message property: This is a production message DataSource password property: duk3ProductionPassword! |
Overriding the Default AWS Parameter Store Configuration
If the default parameter convention does not fit our needs, we can override it using a bootstrap.yml or bootstrap.properties file inside src/main/resources.
This allows us to e.g., override the prefix (default is /config), the name of the application (default is Spring application name) and the profile separator between name and application profile (default is _):
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
aws: paramstore: enabled: true name: other-app-name prefix: /myPrefix profile-separator: '-' |
Updates For Spring Boot 2.4.0
Starting with version 2.4.0, Spring Boot changed some internals in regards to config file processing. There’s a blog post available that discusses the reasoning and changes in detail and also a migration guide.
This change impacts this feature, and from now on, we have to explicitly import the aws-parameterstore as a possible configuration property location:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
spring: application: name: demo config: import: "aws-parameterstore:" |
Summary
Using the Parameter Store of the AWS Systems Manager (SSM), we can easily configure our Spring Boot application thanks to Spring Cloud AWS. With this functionality, we can outsource the configuration of sensitive values to a central place inside AWS.
With the Spring Cloud AWS dependencies, there is almost no further setup required. If you plan to start using it for your application, ensure the following:
- use one of the default provider chains to configure the AWS credentials (e.g., using environment variables)
- configure the same AWS region you used to configure the parameters in the AWS console
- follow the default property naming structure or define your own
You can find the application for this blog post on GitHub.
PS: If your application uses Eclipse MicroProfile, you can achieve something similar by creating a custom ConfigSource using the MicroProfile Config specification.
For more practical hands-on advice on developing Spring Boot applications on AWS, take a look at the Stratospheric project where we develop a real-world application while integrating several AWS services.
Have fun retrieving your Spring Boot application properties using the AWS Parameter Store,
Phil

